Larger applications, when migrating from Windows 7/Windows 2008 R2 or lower to Windows 8/Windows 2012 or higher, may need to consume more resources. The same E3 application, in the same hardware, can stop working due to limits established by a new Windows version.
Cause:
This happens because the default value of Window’s NoInteractiveServices has been changed to 1. Therefore, the E3Server increases it CPU use, which in turn dramatically decreases the number of IOServers supported by E3.
Solution:
Microsoft suggests returning to the previous behavior (Windows 7/Server 2008 R2 or lower), that is, return NoInteractiveServices‘s value to 0 and restart the computer. To do so, follow these procedures:
- In Windows 10 or Windows 8.1, right-click Start and select Run:
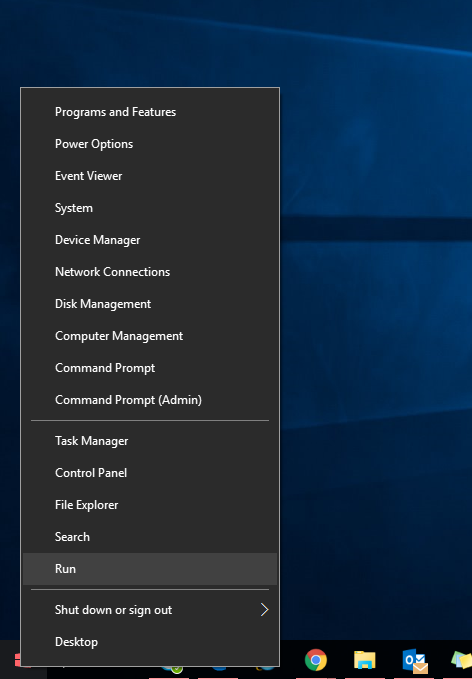
- On Run‘s search box, type:
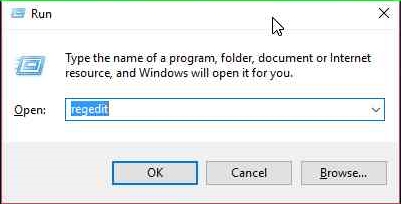
- Press OK to open the Registry:
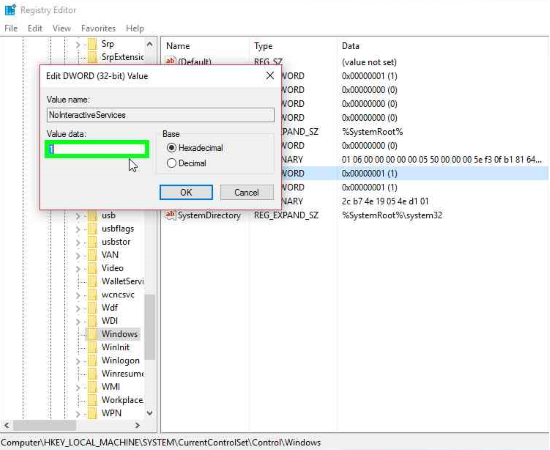
- Find the key at Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \ SYSTEM \ CurrentControlSet \ Control \ Windows \ NoInteractiveServices and change its value to 0.
NOTE: This procedure does not apply to Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows XP, or Windows Server 2003, because its NoInteractiveServices value is 0.
See also:
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn277271.aspx
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/ms683502%28v=vs.85%29.aspx
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/Cc786119%28v=WS.10%29.aspx
https://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/windowsserver/en-US/6fb5693a-a256-41f7-a1df-d30101d9f8b6/unable-to-start-interactive-services-detection-service-in-windows-2012?forum=winserver8gen
http://blogs.msdn.com/b/ntdebugging/archive/2007/01/04/desktop-heap-overview.aspx
http://blogs.technet.com/markrussinovich/archive/2010/02/24/3315174.aspx
